
Fastener coatings specialists must keep up with ever evolving requirements of today’s automotive industry to achieve success in their operations. Here MacDermid Enthone looks at the key criteria that fastener design and corrosion engineers evaluate when choosing coatings for powertrain, exterior, interior and safety critical fasteners. Failure of coatings to meet these criteria could present major challenges to applicators worldwide.
So, what is the key criteria?
Environmental compliance
New coatings must conform to the latest legislative requirements. The primary directives that a coated fastener must comply with are ELV (End of Life Vehicle) Directive, REACH (EU Regulation for the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals), and RoHS (Restriction of the Use of Hazardous Substances). All new coatings are based around sacrificial zinc or alloys, with a trivalent chromium passivate and topcoat free of volatile organic components, and are fully compliant with these environmental needs.
 Performance
Performance
All coatings must exceed defined resistance to both white and red rust. Additionally, depending on the application, the following requirements may be specified:
- Freedom from hydrogen embrittlement.
- Good abrasion resistance (for retention of the surface protection, even when subjected to automated assembly feeds).
- Compatibility with light metals.
- Hardness for thread cutting.
- The ability to be over-painted.
Global availability
As OEMs and their supply chains continue to globalise, the need for applicators applying consistent and reliable coatings is paramount.
Friction properties
Automated assembly demands consistent torque and tension properties. Assessing the requirements of each fastener type in detail can enable understanding of why choosing the right coating is so important.
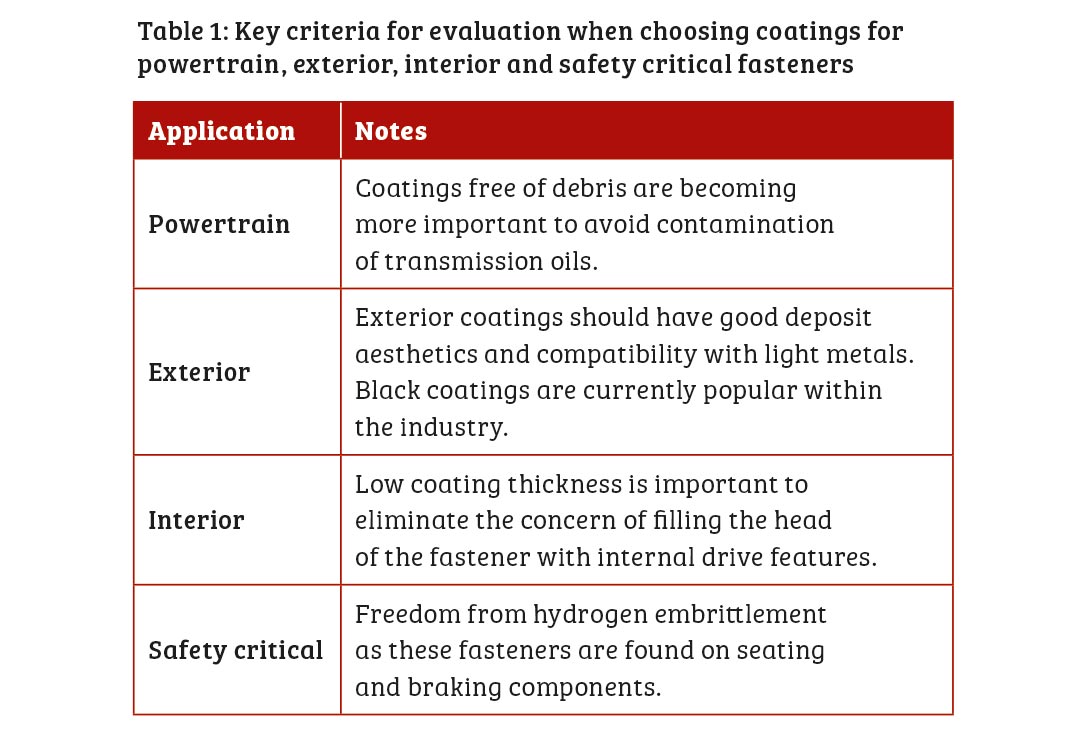
Powertrain fasteners
Powertrain fasteners are located under the hood, around the engine, and within transmission systems. They need to provide good corrosion resistance, heat resistance, oil retention (for internal fasteners) and consistent coefficient of friction properties to ensure maximum joint security, without exceeding the proof load of the fastener. To meet these criteria, either zinc or phosphate coatings may be specified. The former, in conjunction with a suitable dry film lubricant, provides an abrasion resistant coating – which can be used to meet these requirements (and provide a debris free coating). Phosphating is used when the fastener is constantly immersed in oil. For example, for internal fasteners in a gear box, which are not exposed to outside elements.
Exterior fasteners
Exterior fasteners are typically found on the chassis areas, and on the body trim, on the outside of the car – where there is visibility and the highest level of resistance is required. Prolonged exposure to the elements outside, such as sodium chloride, increases the chance of white and red rust on exterior fasteners. Therefore, a long-term solution is critical to ensure reliable protection. Maintaining aesthetic appeal is also important for both end-users and product compliance, due to the prominent position of exterior fasteners.
An increasing number of companies are looking to zinc-nickel for use on exterior fasteners, as demands for improved quality grows. Compared to alternatives, such as organic-based coatings, zinc-nickel finishes offer more control over the thickness of coatings. This allows OEMs to create bespoke high-quality solutions, even on fasteners with fine dimensional tolerances and recessed heads. In comparison with other sacrificial coatings, zinc-nickel also reduces the effect of hydrogen embrittlement – a frequent problem with coatings for exterior fasteners. It also provides the basis for a black coating with extremely good aesthetics.
Interior fasteners
Aesthetic appeal and corrosion protection are important for interior fasteners, as they are equally visible to end users. For components, such as small screws in the dashboard, a sacrificial coating can be effective for both providing a decorative finish or as an adhesive base for paint coatings. Zinc based coatings offer corrosion resistance with a ‘chromium-like’ decorative finish or to provide a base for an organic paint coating. Additionally, zinc-iron may be used as this provides an economical, high performance black coating system with excellent corrosion resistance.
Safety critical fasteners
Component systems, such as wheels, seat belts, steering and suspension, and brake fasteners, all require safety critical fasteners that minimise risk and ensure consistent performance. In this application, mechanical zinc plated deposits are very popular. This process allows steel of any hardness to be processed quickly and effectively, offering the same high protection as more conventional electroplated zinc deposits, without the risk of hydrogen embrittlement.
Conclusion
Today’s fastener design and corrosion engineers are faced with the challenge of evaluating coatings criteria to address applicators’ needs within the automotive industry. To meet such criteria, coatings must be environmentally compliant; be suitable with regards to friction requirements; must all be passivated; and have a top coat or dry film lubricant applied, which is free from any SVHC (Substances of Very High Concern). Finally, these coatings should be available to any suitable applicator worldwide.
At MacDermid Enthone, its ZinKlad programme incorporates all the elements outlined above within its worldwide applicator programme. For more information on the high performance ZinKlad coatings and approved applicators, visit www.zinklad.com

Biog
Will joined Fastener + Fixing Magazine in 2007 and over the last 15 years has experienced every facet of the fastener sector - interviewing key figures within the industry and visiting leading companies and exhibitions around the globe.
Will manages the content strategy across all platforms and is the guardian for the high editorial standards that the Magazine is renowned.








